Whats BIM?
What is BIM? BIM (Building Information Modeling) is an intelligent 3D model-based process that provides architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) professionals the insight and tools to more effectively plan, design, construct, and manage buildings and infrastructure.
Elements of BIM
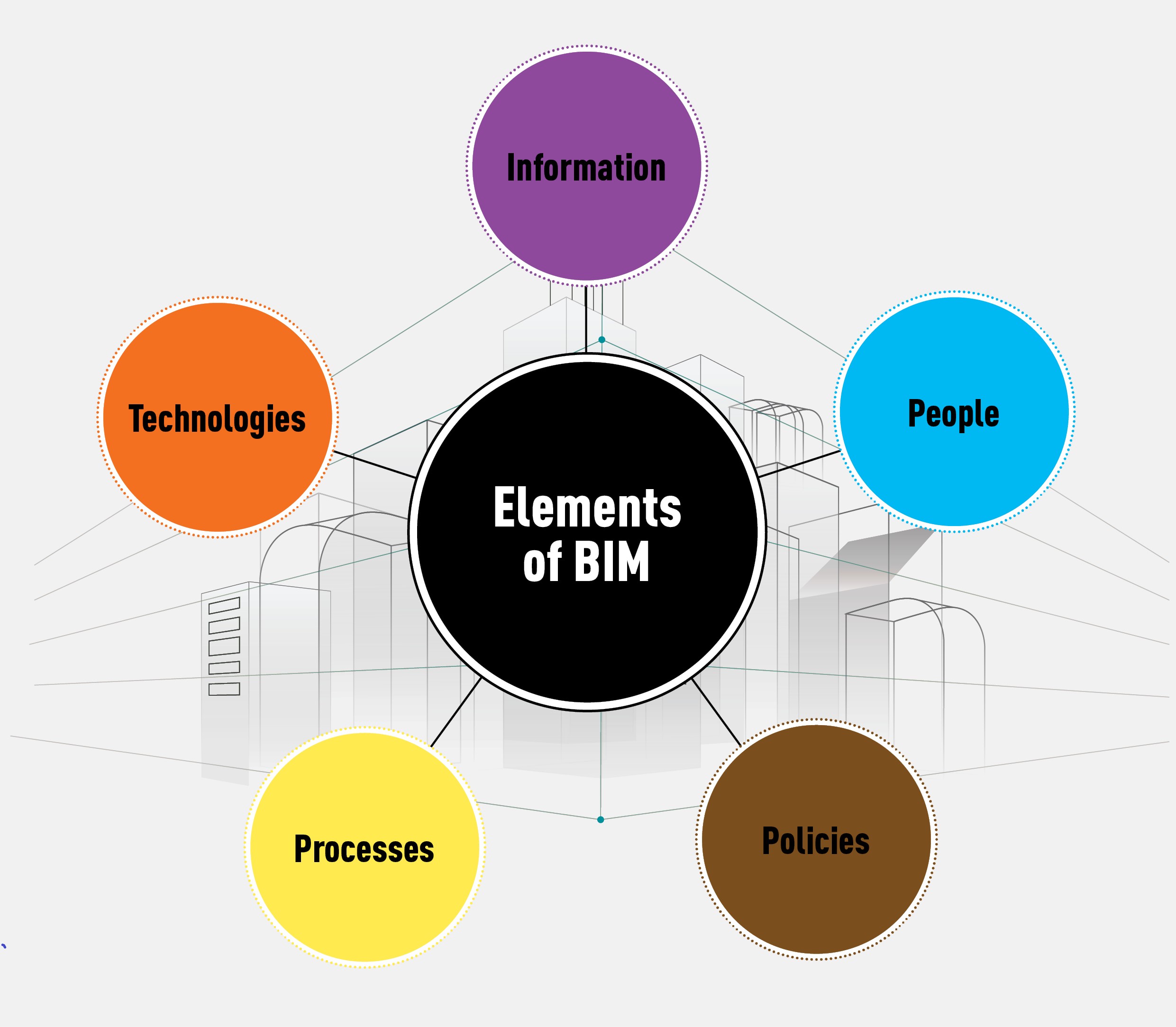
Building Information Modeling refers to a collaborative method of working which is based on the generation and exchange of data and information between the various project parties. For effective functioning, BIM requires integration of the following five elements: Processes, Policies, People, Information and Technologies
Processes refer to the specific order of work activities with a beginning, an end, and a clear identification of the inputs and outputs of each stage.
Policies refer to the principles and rules to guide the decision-making process. Policies are framed to develop standards and best practices to minimize disputes between the parties involved.
People make the difference and therefore are the most important. Effective management by people can only lead to successful BIM. Important people in Building Information Modeling usually include: BIM director, BIM manager, BIM consultant, BIM technologist.
Information: There are two types of information: models and documents. Models are digital data that are the representation, reproduction, or simplified version of an object, road, bridge, building etc. They are stored in a file format and can be exchanged and shared to support the decision-making process for the construction of the infrastructure, buildings etc. Documents are the digital version of papers, drawings, prints, images and video.
Technologies refer to the software and hardware tools used to manage the various stages of the Building Information Modeling process.
Why BIM?
Construction woes take a backseat with Building Information Modeling. It allows more intelligent use of resources, optimization of workflows and leads to productivity and profitability. It allows all interested parties to assess the same information at the same time through the interoperability between different technological platforms. It leads to better outcomes through more effective communication and collaboration.
Be it project management, land surveying, road design, structure design or construction- the role of Building Information Modeling has almost become indispensable for beyond the ordinary results. Using BIM, owners can improve building quality, significantly reduce building lifecycle costs, better understand design projects from beginning to end, optimize operational efficiencies and increase occupancy and use rates.
In construction, Building Information Modeling could be used to monitor the productivity of a construction process. BIM brings the opportunity to try out solutions in advance before building the structure on site: with a constructible model, the structure can be prototyped virtually. Project parties can understand and review the design more easily, which helps guarantee its accuracy and completeness, and visualize and evaluate alternatives in terms of cost and other project parameters. BIM leads to better communication between project parties and better quality.
B for Building
Building Information Modeling has been part of the construction industry for some time now. It is the process of designing a building collaboratively using one coherent system of computer models rather than as separate sets of drawings. BIM is now getting applied to all types of construction, be it buildings, roads, railways, bridges, tunnels etc. Today, we can even apply it to different stages of construction such as planning, design, construction and maintenance.
BIM does not solely refer to buildings, but to all sectors that have to do with construction including: roads, railways, utilities, bridges, tunnels, structures, architecture, topography etc.
I for Information
Information is the heart of Building Information Modeling. BIM changes the way information regarding the entire life cycle of a project and its parts is managed and exchanged. Making available both visual and non-visual information related to every aspect of construction, BIM enables designers, engineers, builders, manufacturers and owners gain a thorough understanding of a project much before its actual construction, thus enabling timely refinement, avoiding errors and generating efficiency.
M for Modeling
We can easily say that the M in Building Information Modeling stands for Model and Management. Using Building Information Modeling, not only a simplified version of an object, structure, building or construction is modelled, but also the process of construction is organized and controlled more effectively.
Key Features of BIM
- Uses 3D models to capture, explore, and maintain consistent and coordinated planning, design, construction, and operational data
- Provides greater project insight for cost, schedule, and constructability
- Uses and shares consistent data whether you’re at your desk or in the field
- Enables prompt response to change with processes that are smarter and faster
Levels of BIM
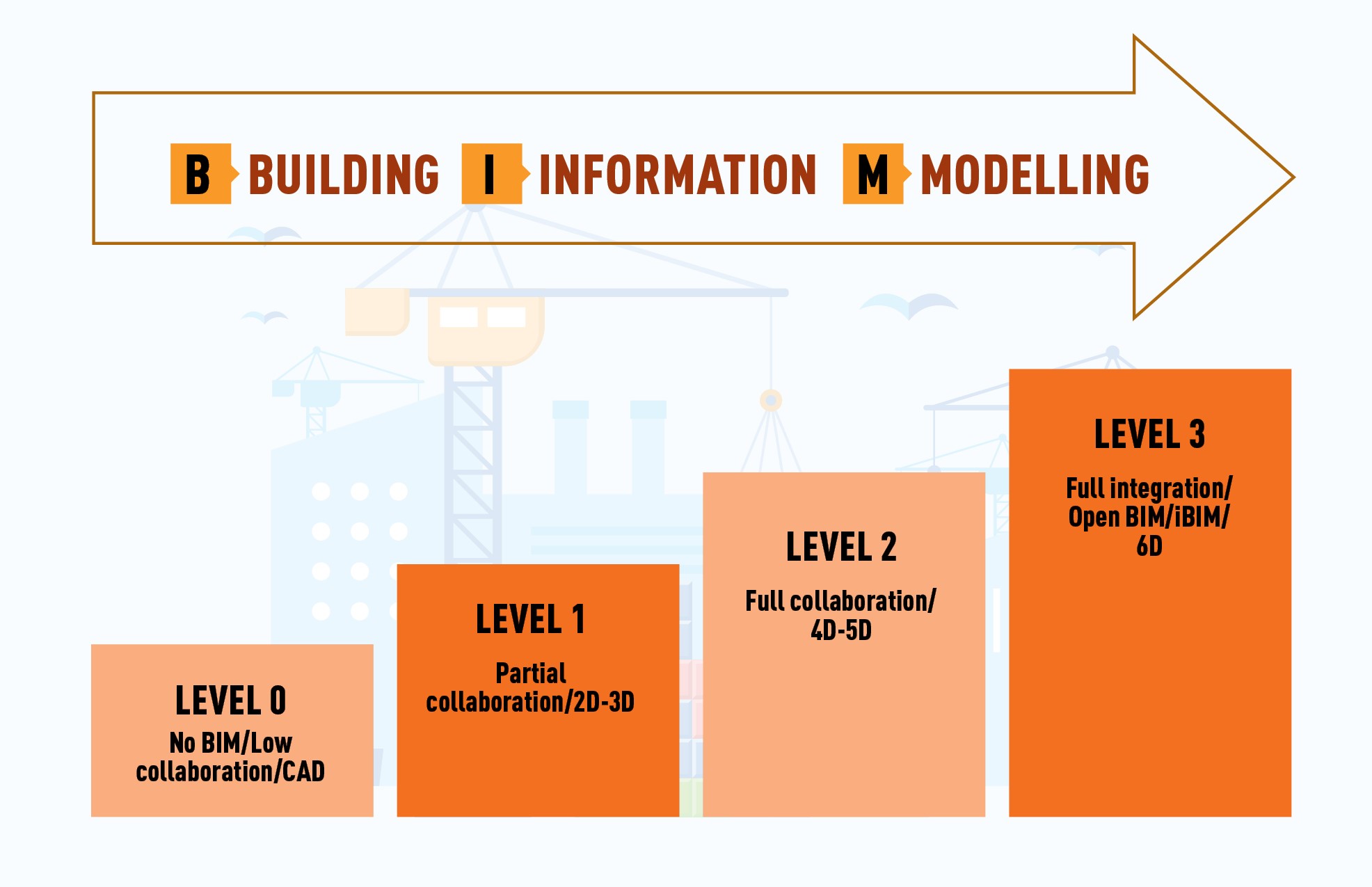
There are currently four levels of Building Information Modeling.
Level 0
BIM Level 0 actually represents a lack of it. At Level 0 there is no collaboration between parties collating information about a built asset. Most data will be 2D (likely CAD) drawings and information exchange is done using paperwork.
Level 1
When data has assumed a form of structure, BIM Level 1 is reached. The CAD is now either 3D or 2D and some collaboration is being achieved between different parties.
Level 2
At Level 2, collaboration is introduced between teams and the process of Building Information Modeling is being followed. There is still a lack of a single source of data, but any data collected about a built asset is shared.
Level 3
At this level, complete and total collaboration in planning, construction and operational life cycle of a built asset is achieved. The data is shared, collected and stored using a single source of data. This universal approach to built asset data is known as ‘Open BIM’ – this is the construction industry’s ultimate goal.
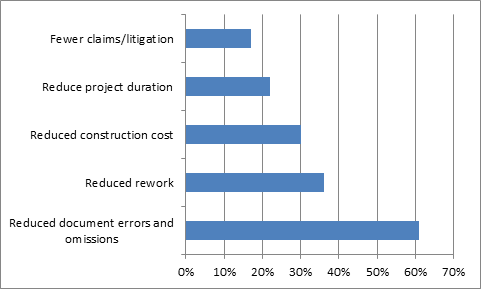
Top benefits of BIM
Future of Building Information Modeling- AI and BIM
With continuous technological advancements, next-generation 6D BIM is one of the essential aspects of creating a flawless futuristic construction. However, what is going to revolutionize and has already done in many cases, is the technologies and processes that digitize the whole process by real-time visualization.
AI has the potential to help reimagine how Building Information Modeling is done. Digging into this a bit deeper, the construction industry is set to benefit in two distinct ways. The first is that AI will support many of the functions common to all business, such as human resources. Second, AI can help with business management to determine demand forecasting and scheduling.
AI techniques can be used to optimize development and quality control testing of products and design structures. To be more productive, construction has to move from being a conceptual model to a constructible model, and this is where technologies like augmented reality or mixed reality will play a big role in enabling the digital engineering process.
Along with this, new building materials, such as self-healing concrete, aerogels, and nanomaterials, as well as innovative construction approaches, such as 3D printing and preassembled modules, can lower costs and speed up construction while improving quality and safety.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=arJp2ma51Wg